Release Notes for Cytoscape 3.7.0

Cytoscape 3.7 is a Cytoscape Desktop version with updated user interface and automation features

Annotations in the form of shapes, images or text can be added to the network canvas. Place annotations in front of or behind the network to create informative visualizations without leaving Cytoscape!
Choose a predefined palette from the Palette picker. These come from published recommendations for choosing colors in scientific and cartographic applications, such as BrewerColors.

New and improved toggles for node, edge, and annotation selection, making it easy to maintain control over stacked network elements without having to shuffle them around.
For Windows and Mac users, if the Cytoscape installer doesn't find a suitable Java Virtual Machine (JVM) already on your workstation, it will download and install one for you. For Linux users, the Cytoscape installer won't download a JVM -- Java 8 (rev 151 or later) must be on the PATH (ahead of any other JVM) or referenced by the JAVA_HOME environment variable.

Automating Cytoscape operations promotes reproducible science, scaling to large numbers of networks, and participation in larger and more complex workflows. As of 3.6, Cytoscape and various apps are callable as services by Python, R and Cytoscape Command scripts.
It is now possible to load networks from an NDEx database directly into Cytoscape (using the Network Search Bar) and to save them directly from Cytoscape (using standard menus). NDEx makes cloud-based sharing and collaboration easy.

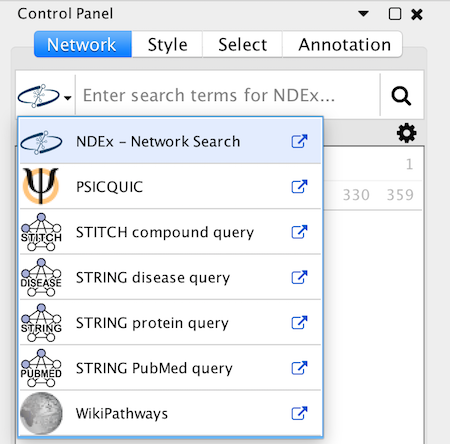
The user interface for loading networks from web-based databases has been dramatically streamlined. Using the new Network Search Bar, you choose the database and enter a query, all from the main Cytoscape network panel. Apps that provide this access include PSICQUIC, NDEx, STRING, STITCH and Pathway Commons.
To load networks and data tables from files, you can simply drag & drop them onto Network Panel / Table Browser.
App developers can create HTML-based material that can appear in a browser-like window within Cytoscape itself, and can access Cytoscape APIs and events.
This heat propagation algorithm uses the network topology to deduce a pertinent set of nodes given a seed set. Subnetworks can then be derived for further investigation.
Use node positions in one network to lay out nodes in another network, thereby simplifying visual network comparison.
Toolbar buttons have illustrative tooltip GIFs to show the functionality of the button.
Select large numbers of nodes much more quickly than in previous versions.
We will no longer be testing Cytoscape releases on 32 bit OSs.
For Windows and Mac users, the Cytoscape installer automatically downloads and installs Java 8 if it's not available on your workstation. For Linux, please use Java 8 as described below.
A bug in Java 8 Update 60 (also present in 65/66) causes scrollbars to not always appear on Linux systems. This occurs on both OpenJDK and Oracle Java releases (including the OpenJDK shipped with Ubuntu 15.10 and some other recent Linux distributions), and is resolved by installing Java 8 Update 72 or later from Oracle.
For Japanese, Korean, and Chinese users, rendering a network to a PDF file can result in loss of labeling information in the PDF. As a workaround, users can generate any type of image file and use the image file instead.
The latest privacy policy is posted here.
On Linux, on the proxy configuration dialog box, fonts are clipped and messages are truncated.
On all platforms, users installing Cytoscape directly from a ZIP or TAR file should manually clear the Cytoscape cache by deleting the CytoscapeConfiguration folder in the user’s home directory.
On all platforms, all Cytoscape session files recorded since v3.0.1 are encoded in UTF-8 instead of the native language encoding. This makes session files portable between workstations in all locales. Users in Japan, Korea, and China are most affected – existing v3.0.0 or v2.x session files must be translated to UTF-8 using a platform-dependent editor (which most users are already using for this purpose). Users in Europe and the Americas are affected, too, if they use characters beyond the standard ANSI 128 – they can translate to UTF-8 using a platform-dependent editor (e.g., Notepad for Windows).
When loading multiple networks into the same network collection, it is important to import tables only after each of the networks is loaded. Interspersing table imports with network loads may cause some table columns to become inaccessible to some networks.
The Cytoscape installer does not run on non-root accounts using the default OpenJDK JVM. It works properly with Oracle Java 8 Update 151 or higher, or as root with OpenJDK. Alternatively, Cytoscape can be installed by downloading and unzipping the GZIP archive found via the Other Platforms link on the Download page.
Fedora 21 (or later) installs a headless (non-GUI) version of Java by default. As a GUI application, Cytoscape will not install or run with this version of Java. To use Cytoscape on Fedora 21 (or later), one will need to install a standard version of Java. The OpenJDK JRE is available from the Fedora package repository - simply install the java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 (for 64-bit) or java-1.8.0-openjdk.i686 (ofor 32-bit) packages. Oracle’s JRE is available for download in RPM format at java.com, though this requires extra configuration.
On Fedora 21 (or later), the Cytoscape splash screen may appear blank on startup. This does not affect the operation of the Cytoscape application, and can be resolved by upgrading to Fedora 23 with latest patches.
Your bug reports are very important to improve quality of future versions of Cytoscape 3. If you notice any problems, please report them from:
Help → Report a bug...
Or, you can directly report it from Report a bug link on the navigation bar.
We need your feedback to improve Cytoscape 3! Please send your questions and comments to our mailing list.